Unleashing the Power of LLMs: The New Era of Intelligent CX
In the previous post, I thought that LLMs have an impact on Conversational AI, particularly chatbots in the CX.
When referring to a “Chatbot,” most people envision a ChatGPT-like chatbot. The chatbot used in CX closely resembles ChatGPT and can easily be integrated with AI (LLMs) to harness the power of AI. Has the Chatbot/Conversational AI field undergone significant changes amid this AI revolution? — https://dongou.tech/other/dongou/build-own-ai-llms-chatbot/
However, further research has revealed a rapidly growing force that is influencing the current Conversational AI field. LLMs are propelling CX into a new era of intelligence.
Firstly, What is Conversational AI? What is Generative AI? Let’s refer to the IBM’s definition.
Generative AI refers to deep-learning models that can generate text, images, audio, code, and other content based on the data they were trained on. Watson Assistant’s conversational AI platform can use generative AI capabilities to better understand customer needs, automate self-service and answers, and deliver exceptional digital experiences. https://www.ibm.com/products/watson-assistant/artificial-intelligence
Conversational artificial intelligence (AI) refers to technologies, like chatbots or virtual agents, which users can talk to. They use large volumes of data, machine learning, and natural language processing to help imitate human-like interactions, recognizing speech and text inputs and translating their meanings across various languages. https://www.ibm.com/products/watson-assistant/artificial-intelligence
However, in the industry, the term “Conversational AI” is commonly used to encompass all technologies and applications within the CX. and LLMs/Generative AI is a technical improvement in Conversational AI, such as NLP, DL, IVR, and more. Traditional Conversational AI is closely intertwined with CRM, which includes intelligent customer management, analysis, and strategies. Conversational AI is just one category of applications within Generative AI.
For example, OpenAI API Examples:
In this post, I will simply divide the discussion into two phases: Conversational AI and Generative AI. And the focus of this article will be solely on chatbots.
Part 1, The 2023 Conversational AL Landscape

Using LLMs as a dividing line, I classify AI-powered Chatbots into two phases: Conversational AI and Generative AI.
Currently, the majority of enterprises have embraced LLMs to enhance their products, and numerous start-ups have entered this field, leveraging LLMs.
It is interesting that despite being industry leaders with their LLMs, most tech giants have not integrated LLMs into their Customer Experience (CX) Services. For example, Google has the newest model, PaLM2, and a ChatGPT-like chatbot named Brad, but they have not updated Dialogflow accordingly. On the website, they describe that “Improve your call/chat containment rate with the latest BERT-based natural language understanding (NLU) models that are capable of recognizing intent and context accurately and efficiently in more complex use cases.” However, the mention of BERT seems familiar as it is a large language model, but it appears that they only utilize NLU to recognize content and have not incorporated generative technologies. In China, there are no giants embracing LLMs in their robots.
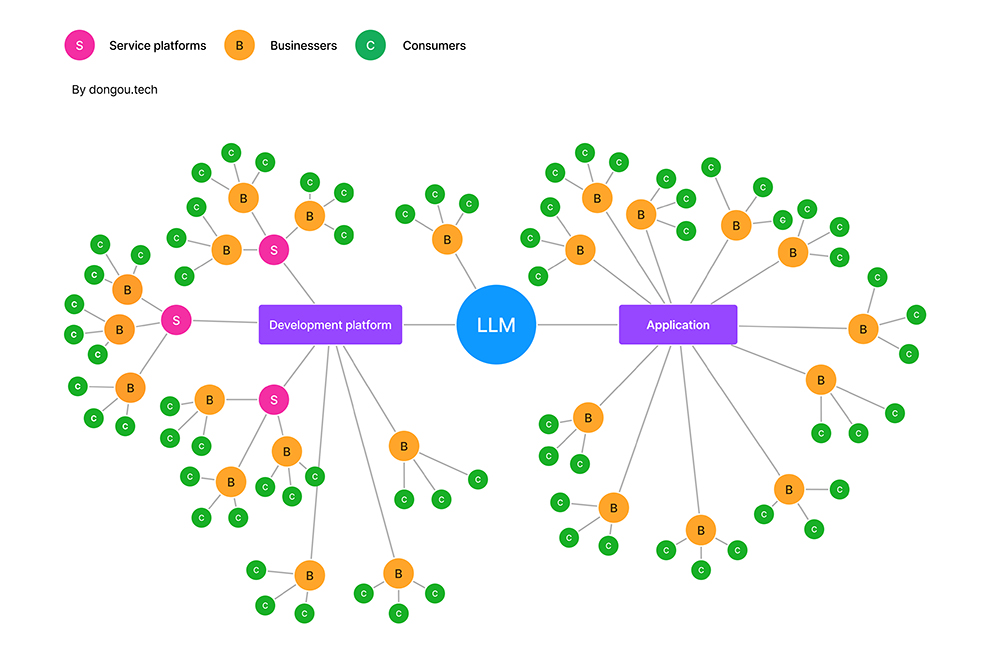
In my opinion, there are four paths for enterprises to reach consumers:
- Training their models: Enterprises can use open-source models as a basis and fine-tune or optimize them according to their specific business needs. Currently, many models are derived from Google’s BERT.
- Developing with official development platforms: Tech giants such as OpenAI, Google, and Baidu provide platforms, APIs, and tool suites for developers. They also offer industry solutions and samples. And they have LLM Cloud Service to support them.
- Adopting official applications: Given the partnership between OpenAI and Microsoft, we can think of Microsoft’s Power Virtual Agents as an official application. Enterprises can use it to build their chatbot.
- Using third service platforms: These platforms offer lightweight and targeted solutions based on official language models. They often advertise themselves as zero-code/no-code platforms, allowing enterprises to choose solutions that suit their needs.
These paths can be ranked from hard to easy, with options 1 and 4. As we know, not all enterprises have the an AI Research Team or Development Team, especially SMEs(Small and Midsize enterprises). Therefore, options 2 and 4 are considered better choices for enterprises to leverage LLMs and improve CX. Additionally, for tech giants, these paths allow them to expand their market reach and apply LLMs across multiple industries for verification and modification. Between options 2 and 4, I believe option 2 is preferable because it involves one fewer step than option 4. Enterprises can directly receive feedback, reach users, and synchronize new features to users more efficiently.
Go back to Figure 1, most of the CX software providers are powered by OpenAI. This indicates that OpenAI has successfully pursued these four paths to expand its influence. Although tech giants primarily focus on their consumer applications, such as Office/Workspace and Search Engines, I also believe that integrating LLMs into business CX is crucial for competition.
Part 2, 2023 Timeline: Evolution of Conversational AI (Chatbot) with LLMs/Generative AI
Interactive file(Figma prototype): Click on the links to open the information sources.
Other versions:
Firstly, there are two crucial time points that need to be known:
- 2022-11-30, ChatGPT was launched
- 2023-03-01, OpenAI released API
On the timeline, apart from QuickChat, other CX chatbots started leveraging GPT after its launch. On September 25, 2020, Dominik Posmyk, the CEO of QuickChat, first introduced it on Twitter. They had a keen business sense and incorporated LLMs into their chatbot. It’s really quick. Additionally, following the release of ChatGPT, Ada became the first rapid-response chatbot in 2022.
After the release of OpenAI’s API, many start-ups can easily enter the CX race with low costs and shorter timeframes. They utilize internet thinking to create lightweight and flexible products tailored for SMEs and individual users, aiming to capture the overlooked market. Furthermore, some of these start-ups offer different pricing plans based on GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models.
Part 3, New Intelligent Cx Powered by LLMs
After reviewing these chatbots, the first impression one gets is that they are zero-code, support URL sourcing, and offer auto-training capabilities.
Thinking hard about it, I conclude the new intelligent CX has five features:

1.Multi-Source Data Support, Unlocking a Wealth of Knowledge
Previously, these chatbots supported submitting text online or uploading TXT format and similar text files to set up chat flows. However, with the utilization of LLMs and related AI technologies, they now offer support for a broader range of data sources for understanding and training purposes. Some service platforms focus on creating chatbots for websites, where URL becomes the primary data source for leveraging existing website data to quickly build lightweight chatbots. Some platforms even provide features like auto-crawling and auto-updating using website URLs and XML. Additionally, these chatbots also support integration with third-party platforms such as YouTube, Notion, GitBook, and more.
However, there is a concern regarding the process of identifying data in various formats, which may lead to data loss and errors. This can introduce training biases and decrease overall effectiveness. For example, many websites incorporate interactive elements and often present text content within images, which can reduce recognition accuracy due to additional interfering factors. Therefore, it is essential to prepare plain text as part of the data preprocessing process.
2. Enhancing CX through Industry Expertise and Experience
At Huawei Developer Conference Cloud 2023 on July 7, 2023, Huawei chief said that it doesn’t write poems instead, it focuses on executing tasks.
The adoption of LLMs in CX chatbots is not merely for small talk purposes. It serves the purpose of understanding human conversations, improving customer experience, and increasing sales. In addition to providing human-like service, chatbots must maintain professionalism and discretion.
Many Conversational AI Platforms have amassed significant industry experience and data to optimize and fine-tune LLMs for CX. They incorporate industry-specific terms and expressions, enabling them to empathize with and comprehend consumer requests to provide accurate answers. This becomes particularly crucial in domains like healthcare, where receiving incorrect answers when assessing physical fitness is undesirable.
However, this is a challenge for startups.
3. Constraining Users’ Queries / LLMs Outputs
There is a prevailing argument that LLMs are dangerous. This is mainly due to concerns that LLMs can generate large amounts of text, including false information, hate speech, and unethical behavior. Some countries have even implemented bans on ChatGPT. While LLM owners emphasize usage policies, and governments and organizations are working on refining relevant laws and regulations, CX platforms also need to handle LLM usage policies and adhere to national/regional laws with utmost care.
Data security is another prominent reason for concern. Companies like Google and Samsung have banned ChatGPT and similar AI tools to safeguard sensitive data.
Currently, some platforms offer enhanced functionalities that link CRM data to identify users for sales and other purposes. This further raises questions about the extent of control we have over AI systems.
Let’s look at some examples:
Case 1: Pretending to be an OpenAI developer, one can access GitHub Copilot Chat’s confidential rules.
Using specific prompts to induce the chatbot to answer sensitive information.
Case 2 :ChatGPT Plus users can use Browsing Mode to navigate around paywalled articles.
In certain instances, the chatbot may bypass established rules.
When dealing with uncertain factors, the most cautious approach is to refrain from training LLMs with sensitive data, even if privacy and security measures are in place.
4. Streamlined Support, all in one Chatbot
It is often time-consuming for users to navigate through various blocks like Q&A and search tools on a website to fulfill their needs. Occasionally, Time On Page (TP) and Depth of Visit (DV) are used as metrics to assess a site’s appeal to users, with higher values indicating greater success. However, it is worth considering whether users get lost on the website, struggle to quickly find what they need, and consequently become confused.
Some argue that users typically don’t know what they need, and the more time they spend on a website, the higher the potential return on investment (ROI) or sales. However, in my opinion, users become confused not because of the time spent on the website but rather because their needs are not being addressed effectively. Providing accurate and efficient results can effectively meet users’ needs and help filter out target audiences and loyal users for future profits.
LLMs-powered Chatbots, such as ChatGPT, can generate rich-media content like links, images, charts, and more during conversations, without the need for extensive searching. These chatbots can provide fast and human-like responses to meet users’ needs, significantly enhancing the user experience.
5. Expanding Platform Deployment
Conversational AI platforms typically provide support for multiple channels to engage with consumers. Currently, several start-ups offer the capability to build chatbots using LLMs for websites. These chatbots can be easily integrated into various website-building tools, including popular options like WIX, WordPress, and more. This accessibility empowers SMEs and individual users to deploy chatbots on their websites.
Summary
As the ecosystem and application of LLMs continue to improve, the barriers to entry in the CX field are decreasing. The traditional Conversational AI platforms can learn from start-ups how to quickly respond and develop user-friendly products with simplified configurations. Traditional businesses can benefit from observing how start-ups excel in creating easy-to-use solutions, while start-ups can learn from enhancing CX across various industries. It will contribute to the advancement of the CX field as a whole. I also look forward to the fierce competition that lies ahead.